
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Select Language
USD 25 ~ USD 30
Brand:N
Model No:AV01
Transportation:Ocean,Land,Air,Express
Packaging:PLASTIC BAGGED
Supply Ability:5000KG/M
Place of Origin:CN
Productivity:10,000KG/M
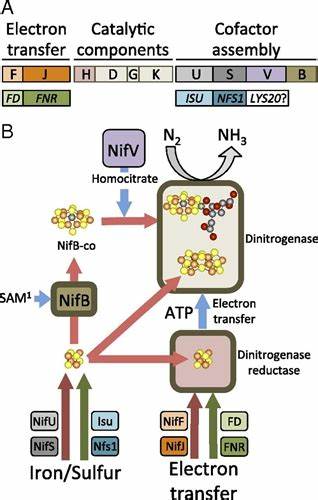
Introduction Soon after the discovery of Azotobacter vinelandii in 1903 [1], it was adopted as a model organism for the study of aerobic nitrogen fixation, respiration, microbial physiology, hydrogen production and assimilation, and other enzyme...
The utilization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) in agriculture is continuously increasing as it offers an effective tool to replace the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides and other harmful supplements (Ansari et al., 2017, Ansari and Mahmood, 2019a). Growth promoting substances are produced in huge quantities by the action of these rhizosphere microorganisms that directly or indirectly influence the overall morphology and physiology of the crops. Recent advances in the field of sustainable development relies on the use and diversity of PGPR, their colonizing capability and the mechanism of action that may be used to facilitate their application as a dependable element in the management of sustainable agricultural system.
Azotobacter is a group of Gram negative, free-living, nitrogen fixing aerobic bacteria inhabiting in the soil. They are oval or spherical in shape and form thick-walled cysts (dormant cells resistant to deleterious conditions) under unfavorable environmental conditions. Around six species in the genus Azotobacter have been reported, some of which are motile by means of peritrichous flagella while others are immotile . They are typically polymorphic having size ranging from 2 to 10 µm long and 1 to 2 µm wide. The genus Azotobacter was recognized in 1901 by Dutch microbiologist, botanist and founder of environmental microbiology-Beijerinck and his co-workers as the first aerobic free-living nitrogen fixer. These bacteria are known to exploit atmospheric nitrogen for their cellular protein synthesis which is mineralized in the soil, imparting the crop plants a considerable part of nitrogen available from the soil source. Azotobacter spp. is sensitive to acidic pH, high salt concentration and temperature . They pose advantageous impacts on the crop growth and yield through the biosynthesis of biologically active substances, instigation of rhizospheric microbes, production of phytopathogenic inhibitors, alteration of nutrient uptake and eventually magnifying the biological nitrogen fixation . Research on Azotobacter chroococcum in crop production has shown its importance in improving plant nutrition and amelioration of soil fertility . Several strains of Azotobacter are found to be able to produce amino acids when grown in culture media supplemented with various carbon and nitrogen sources . Such substances produced by these rhizobacteria are implicated in several processes thus leading to plant-grown promotion . The scope of utilizing Azotobacter chroococcum in research experiments as microbial inoculant through release of growth substances and their impact on the plant has markedly improved crop production in agriculture.

Certificate





Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.